News
German MBE Workshop 2021

Scienta Omicron is looking forward to participating as exhibitor on the 2021 German MBE Workshop. The Workshop will be organised by the Physics department of the University of Göttingen as a virtual conference. Continuing the longstanding tradition of an annual meeting for the German speaking MBE community, the main objective is to provide a platform for young researchers, where they can present their work and discuss it with leaders in their respective fields.
POLAR SPM Lab: Low Temperature SPM with Unsurpassed Hold Time
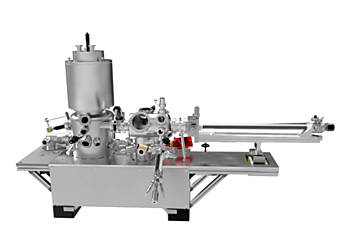
The key features include: STM, QPlus® AFM & Spectroscopy; Guaranteed Helium Holding Time: >200 h; Integrated TRIBUS Head; Sample and Tip Temperature T <5 K; Vertical Magnetic Field: B = ±5 T; and Independent Tip and Sample Exchange.
Molecular Beam Epitaxial (MBE) Growth of Topological Materials
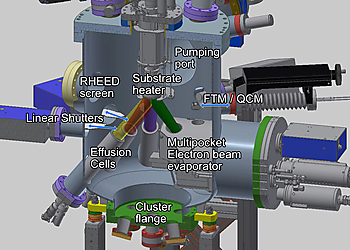
Scienta Omicron’s MBE and In-Situ Surface Analysis Solutions Facilitate Future Development. Topological materials are a significant focus in today‘s condensed matter physics, as pointed out in the excellent perspective article recently compiled by Matthew Brahlek et al. Scienta Omicron is proud to contribute with integrated MBE and surface analysis instruments to the investigation and development of topological materials.
Secret Behind One of the World’s Toughest Materials
A team of scientists led by Nanyang Technological University (NTU Singapore) and Rice University in the US, has uncovered the key to the outstanding toughness of hexagonal boron nitride (h-BN). It can withstand ten times the amount of force that graphene can, which is known as one of the toughest materials on Earth.
